VIDEOS
NOTES


ASSIGNMENT
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (1 mark each)
- Which of the following is a product of Wurtz reaction?
a) Alkene
b) Alkyne
c) Alkane
d) Alcohol - Which reagent gives elimination as the major product with 2-bromopentane?
a) Aqueous KOH
b) Alcoholic KOH
c) KCN
d) AgNO3 - SN1 mechanism is favored by:
a) Primary halides
b) Secondary halides
c) Tertiary halides
d) All halides equally - Which of the following reacts with haloarenes in Wurtz-Fittig reaction?
a) Another aryl halide
b) Sodium alkoxide
c) Alkyl halide + Na
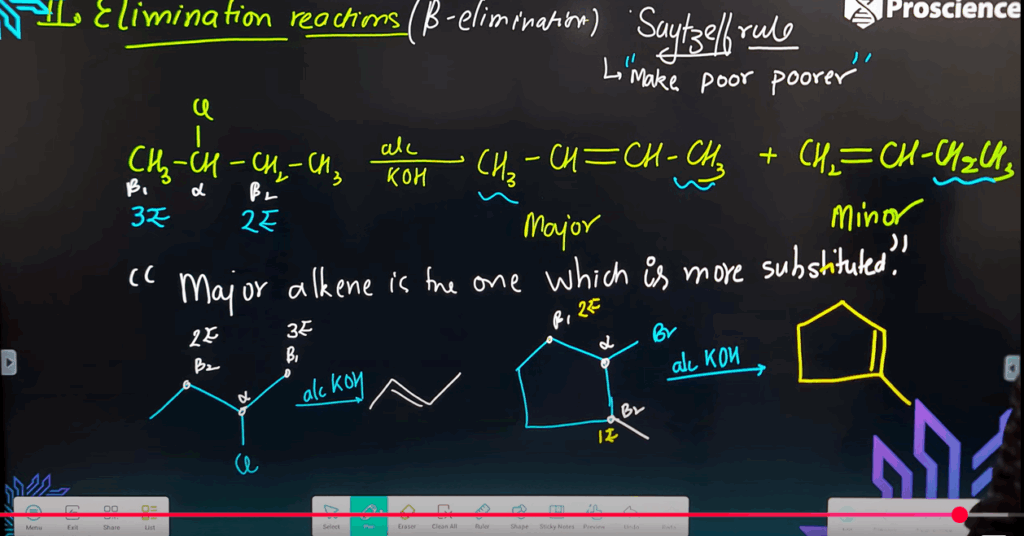
d) Sodium nitrite - The elimination reaction of 2-bromobutane in alcoholic KOH gives:
a) Butan-2-ol
b) But-1-ene and But-2-ene
c) Butane
d) 2-chlorobutane
Section B: Assertion and Reason (1 mark each)
- Assertion (A): Alcoholic KOH induces β-elimination in haloalkanes.
Reason (R): The OH⁻ acts as a base and abstracts a proton. - Assertion (A): SN2 reactions are faster in primary alkyl halides.
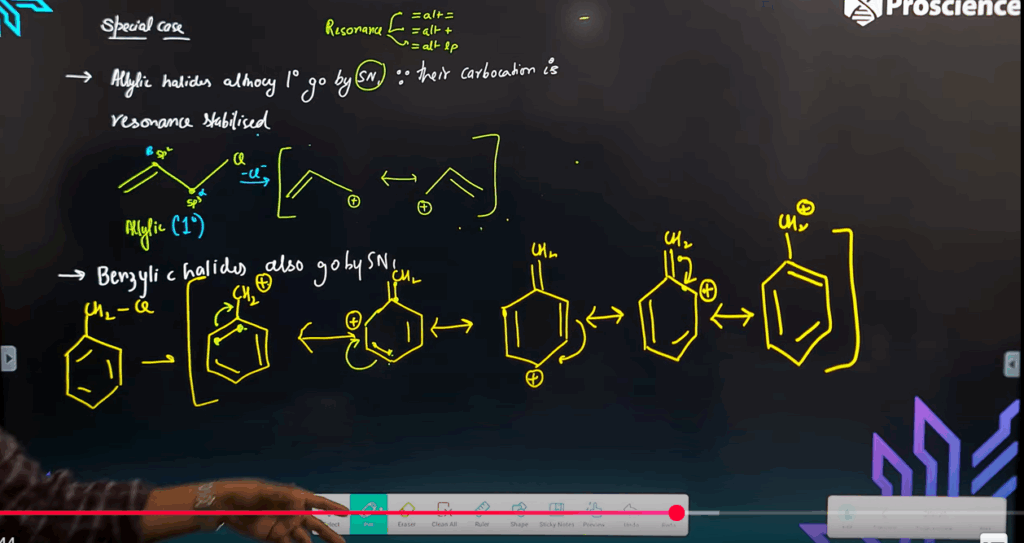
Reason (R): Less steric hindrance allows easy backside attack. - Assertion (A): Aryl halides do not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution.
Reason (R): Resonance stabilization and partial double bond character in C–X bond.
Section C: One Word/One Line Answer (1 mark each)
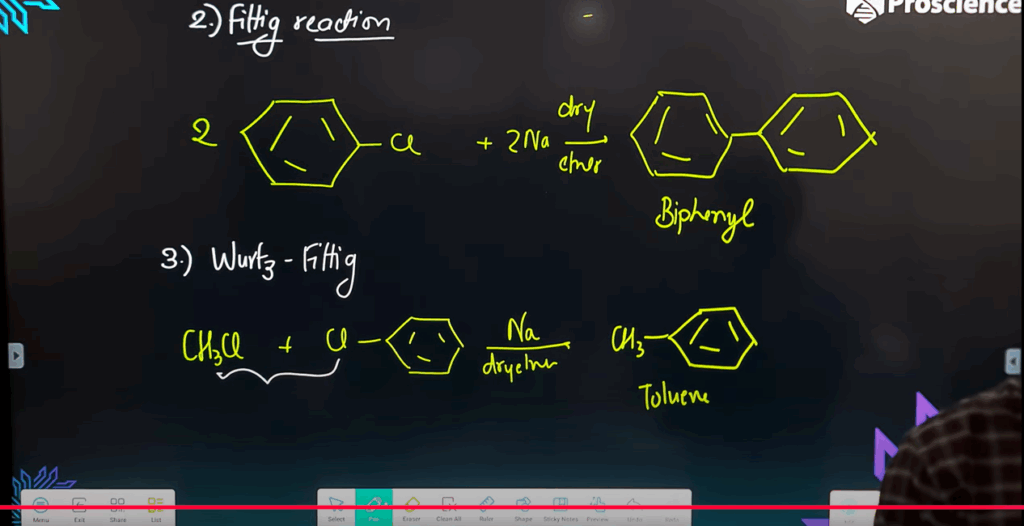
- Name the reaction: Alkyl halide + Na + Alkyl halide → Alkane.
- What is the role of dry ether in Wurtz reaction?
- What type of product is obtained when haloalkane reacts with alcoholic KOH?
Section D: Short Answer Questions (2 marks each)
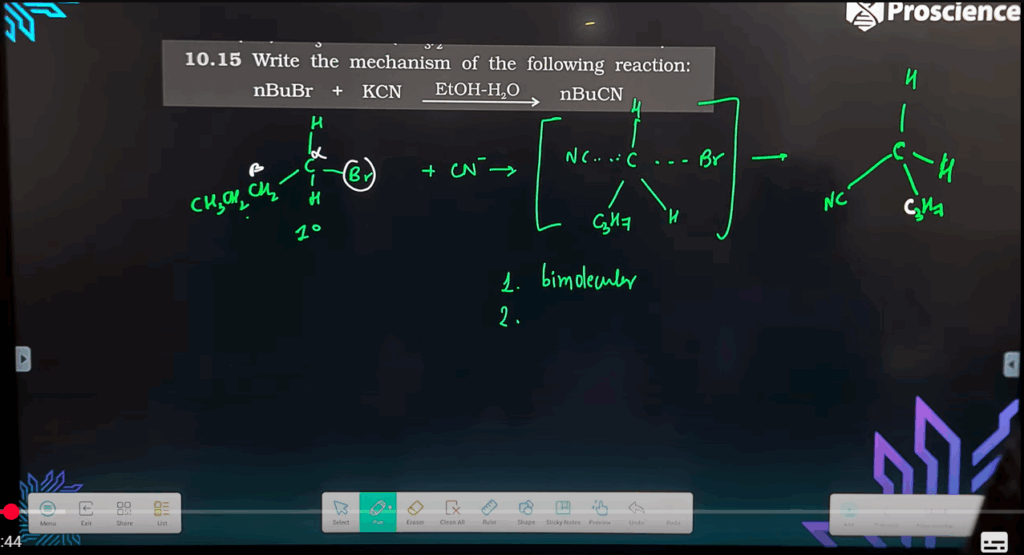
- Explain with an example the difference between SN1 and SN2 mechanisms.
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the Wurtz-Fittig reaction and name the product.
Section E: Short Answer Question (3 marks)
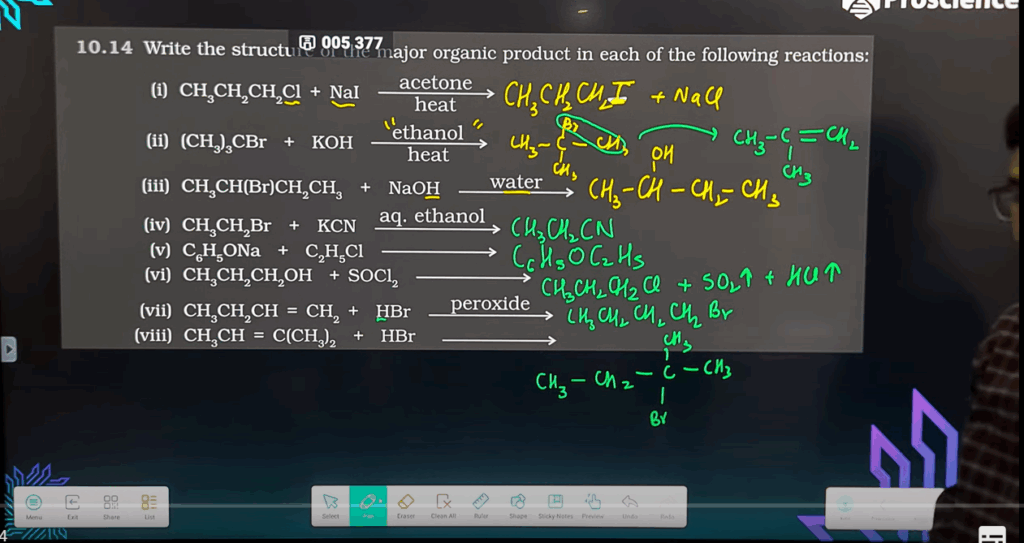
- Complete and write the products for the following reactions:
(a) C2H5Br + alcoholic KOH → ?
(b) Bromobenzene + CH3Br + Na (in dry ether) → ?
(c) C2H5Br + KCN → ?
KEY
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions
- Answer: c) Alkane
- Answer: b) Alcoholic KOH
- Answer: c) Tertiary halides
- Answer: c) Alkyl halide + Na
- Answer: b) But-1-ene and But-2-ene
Section B: Assertion and Reason
- Answer: a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation.
- Answer: a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation.
- Answer: a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation.
Section C: One Word/One Line Answers
- Answer: Wurtz reaction
- Answer: Solvent and reaction medium for the sodium metal
- Answer: Alkene (via β-elimination)
Section D: Short Answer Questions
- Answer:
– **SN1** is a two-step mechanism, involves carbocation intermediate, e.g., (CH₃)₃CBr → (CH₃)₃COH
– **SN2** is a single-step backside attack with inversion, e.g., CH₃CH₂Br + OH⁻ → CH₃CH₂OH - Answer:
C₆H₅Br + CH₃Br + 2Na → C₆H₅CH₃ + 2NaBr
(This is the **Wurtz-Fittig reaction**; product is toluene)
Section E: Short Answer Question (3 Marks)
- Answer:
- (a) C₂H₅Br + alcoholic KOH → CH₂=CH₂ + HBr + H₂O (Ethene formed via β-elimination)
- (b) C₆H₅Br + CH₃Br + 2Na → C₆H₅CH₃ + 2NaBr (Toluene via Wurtz-Fittig reaction)
- (c) C₂H₅Br + KCN → C₂H₅CN + KBr (Ethyl cyanide via nucleophilic substitution)
