VIDEOS
NOTES

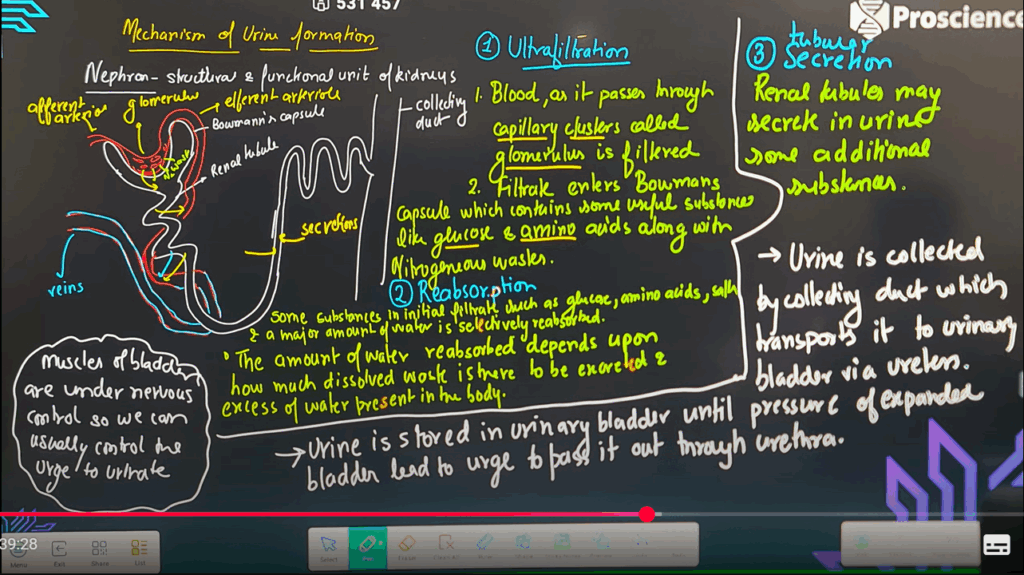


ASSIGNMENT
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (1 mark each)
- The basic filtration unit of the kidney is called:
a) Neuron
b) Nephron
c) Alveoli
d) Tubule - The process of filtration in the glomerulus is called:
a) Assimilation
b) Transpiration
c) Ultrafiltration
d) Dialysis - Maximum amount of reabsorption takes place in:
a) Loop of Henle
b) Distal Convoluted Tubule
c) Collecting Duct
d) Proximal Convoluted Tubule - Which part of the nephron is involved in the secretion of ions like H+ and K+?
a) Glomerulus
b) Bowman’s capsule
c) Tubular cells
d) Ureter - The artificial kidney works on the principle of:
a) Active transport
b) Osmosis
c) Diffusion across a semi-permeable membrane
d) Transpiration pull
Section B: Assertion and Reasoning (1 mark each)
Choose the correct option:
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false but R is true
- Assertion (A): Ultrafiltration occurs in the glomerulus.
Reason (R): Blood pressure forces plasma out of capillaries into Bowman’s capsule. - Assertion (A): Reabsorption of useful substances takes place in nephrons.
Reason (R): Reabsorption is a passive process in all cases.
Section C: One-Word Answer (1 mark each)
- Name the nitrogenous waste product filtered out in urine.
- What is the total amount of filtrate produced in kidneys per day?
- What is the volume of urine excreted daily by a healthy adult?
Section D: Short Answer Questions (2 marks each)
- What is the role of proximal convoluted tubule in reabsorption?
- What is tubular secretion? Mention its importance in urine formation.
- Why is the glomerular filtration called ultrafiltration?
Section E: Long Answer Questions (3 marks each)
- Explain the mechanism of urine formation briefly under the following headings:
a) Ultrafiltration
b) Reabsorption
c) Tubular secretion - Describe the structure and working of an artificial kidney. How is it different from natural nephron in terms of reabsorption?
KEY
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions
- b) Nephron
- c) Ultrafiltration
- d) Proximal Convoluted Tubule
- c) Tubular cells
- c) Diffusion across a semi-permeable membrane
Section B: Assertion and Reasoning
- a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation
- c) A is true but R is false
(Reabsorption involves both passive and active transport)
Section C: One-Word Answer
- Urea
- 180 litres
- 1.5 litres
Section D: Short Answer Questions
The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) reabsorbs glucose, amino acids, salts, and a major portion of water from the filtrate. It helps in minimizing water and nutrient loss.
Tubular secretion is the active transport of substances like H+, K+, and drugs from blood into the renal tubule. It helps maintain pH and remove toxins.
Glomerular filtration is termed ultrafiltration because it occurs under high pressure and filters small molecules like water, glucose, salts, and urea from blood into Bowman’s capsule.
Section E: Long Answer Questions
a) Ultrafiltration: Blood enters glomerulus under pressure; plasma is filtered into Bowman’s capsule.
b) Reabsorption: Essential nutrients, water, and salts are reabsorbed into capillaries mainly in PCT.
c) Tubular Secretion: Additional wastes like ions and drugs are secreted into the tubule from capillaries.
Structure & Working of Artificial Kidney (Dialyzer):
- Blood is pumped from the patient to a machine containing a dialyzing membrane.
- Waste products and excess salts diffuse across the membrane into the dialyzing fluid.
- Clean blood is returned to the body.
Difference from Nephron:
- Artificial kidney lacks selective reabsorption, which occurs naturally in nephron, especially in PCT and loop of Henle. It can’t reabsorb glucose or fine-tune water content.
