VIDEOS
NOTES


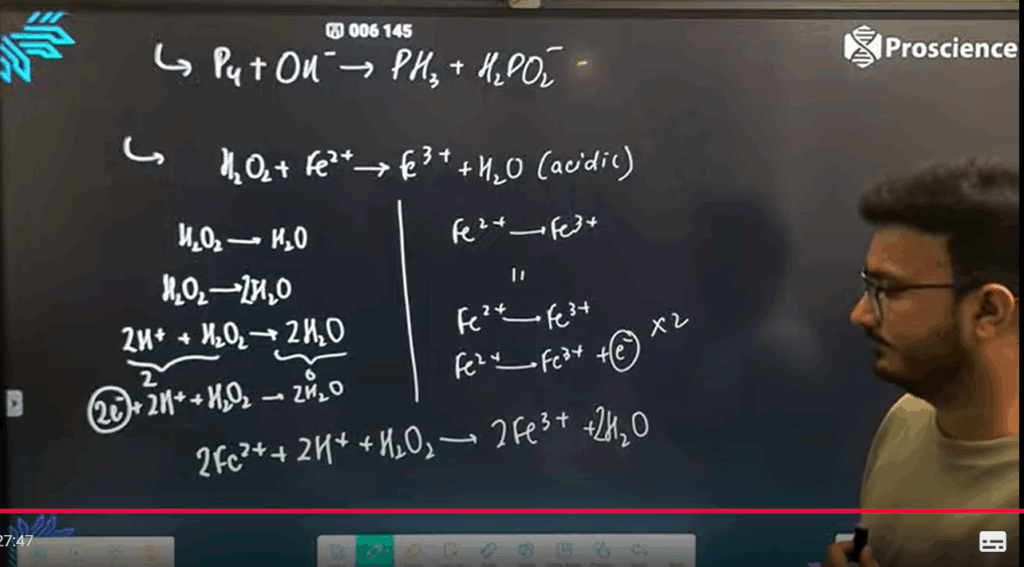
ASSIGNMENT
Section A: Very Short Answer Questions
- Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron transfer.
- What is meant by a redox reaction?
- In the reaction:
Zn(s) + CuSO₄(aq) → ZnSO₄(aq) + Cu(s),
identify the species oxidised and reduced. - What is a half reaction?
- Name the oxidising and reducing agents in:
Cl₂(g) + 2NaBr(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + Br₂(l)
Section B: Short Answer Questions (2 Marks Each)
- Write the oxidation and reduction half reactions for the following overall redox reaction:
Fe²⁺ + Ce⁴⁺ → Fe³⁺ + Ce³⁺ - Identify the oxidant and reductant in the following reaction:
H₂S(g) + Cl₂(g) → 2HCl(g) + S(s) - Balance the following redox reaction using the half reaction method (in acidic medium):
Fe²⁺ + Cr₂O₇²⁻ + H⁺ → Fe³⁺ + Cr³⁺ + H₂O - Balance the following redox reaction by half reaction method in basic medium:
MnO₄⁻ + I⁻ → MnO₂ + I₂ - Explain why redox reactions are always coupled reactions.
Section C: Application-Based Questions (3 Marks Each)
- Identify oxidation and reduction half reactions in:
2Cu₂O + Cu₂S → 6Cu + SO₂
Also name the oxidising and reducing agents. - Balance the following redox reaction using the half reaction method in acidic medium:
Cr₂O₇²⁻ + SO₃²⁻ → Cr³⁺ + SO₄²⁻ - Define the following with examples:
a) Oxidising Agent
b) Reducing Agent
c) Redox Reaction - Classify the following reactions as combination, decomposition, displacement or disproportionation redox reactions:
a) Cl₂ + 2OH⁻ → Cl⁻ + ClO⁻ + H₂O
b) 2Na + Cl₂ → 2NaCl
c) 2KClO₃ → 2KCl + 3O₂ - Explain the role of electrons in balancing redox equations using the Fe²⁺ and MnO₄⁻ redox couple in acidic medium.
KEY
Section A: Very Short Answer Questions
- Oxidation: Loss of electrons
- Reduction: Gain of electrons
A redox reaction is a chemical reaction in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
- Zn is oxidised: Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻
- Cu²⁺ is reduced: Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
A half reaction shows either the oxidation or the reduction part of a redox process, including electron transfer.
- Oxidising agent: Cl₂ (gets reduced)
- Reducing agent: Br⁻ (gets oxidised)
Section B: Short Answer Questions
Oxidation half: Fe²⁺ → Fe³⁺ + e⁻
Reduction half: Ce⁴⁺ + e⁻ → Ce³⁺
- Oxidising agent: Cl₂ (gets reduced to HCl)
- Reducing agent: H₂S (gets oxidised to S)
Balanced (acidic):
6Fe²⁺ + Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 14H⁺ → 6Fe³⁺ + 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O
Balanced (basic):
2MnO₄⁻ + 3I⁻ + 2H₂O → 2MnO₂ + 3I₂ + 4OH⁻
Redox reactions involve electron transfer. Since electrons lost in oxidation must be gained in reduction, both processes occur together (coupled).
Section C: Application-Based Questions
Oxidation: S in Cu₂S → SO₂
Reduction: Cu⁺ in Cu₂O → Cu
- Reducing agent: Cu₂S
- Oxidising agent: Cu₂O
Balanced:
Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 3SO₃²⁻ + 8H⁺ → 2Cr³⁺ + 3SO₄²⁻ + 4H₂O
a) Oxidising Agent: Species that causes oxidation, e.g., KMnO₄
b) Reducing Agent: Species that causes reduction, e.g., Zn in Zn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu
c) Redox Reaction: Any reaction involving both oxidation and reduction
a) Disproportionation
b) Combination
c) Decomposition
Fe²⁺ → Fe³⁺ + e⁻ (oxidation)
MnO₄⁻ + 5e⁻ + 8H⁺ → Mn²⁺ + 4H₂O (reduction)
Electrons lost = electrons gained → balance redox
